
Using splints and undertaking follow-up gives EXACTLY the same results as no splints and no follow-up-but splints and follow-up is associated with inconvenient and unnecessarily uses resources.” “This has shown us that more isn’t always better. Perry the data confirmed that, as he put it, more is not always better. The research team also found no significant difference in the pain scores at any time during the six-week follow-up period and no significant differences in patient self-reported function.įor Dr. The data showed that at three days after treatment, pain scores were equivalent for children treated with a bandage and immediate discharge to those treated with rigid immobilization and routine follow-up. The team, using a randomization technique, then pulled pain and function data for 489 children who had been treated with bandages (such as a gauze roller bandage) and 476 who’d been treated with rigid immobilization (rigid wrist splint). A buckle fracture, sometimes called a torus fracture or compression fracture, occurs when a bone has been compressed, most often from a fall, causing the.
#TORUS FRACTURE TRIAL#
Using the Forearm Fracture Recovery in Children Evaluation (FORCE) trial which had been conducted in 23 emergency departments in the UK, the researchers collected data from children between the ages of 4–15 years who had presented with distal radius torus fractures. Furthermore, unnecessary casts or splints and follow-up are not only inconvenient, but also harmful to the environment.”
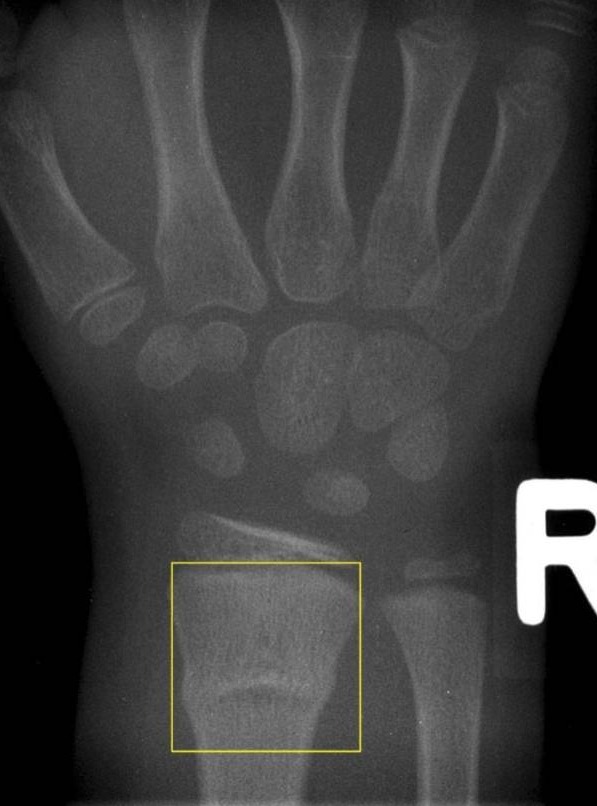
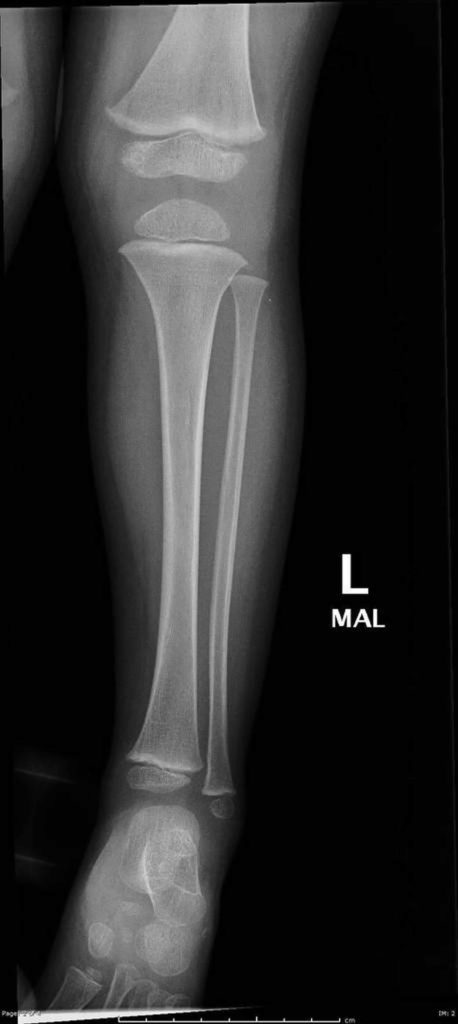
“COVID has shown us the pressure that hospitals are under, and stopping unnecessary follow-up is good for families and for the hospital systems. (Hons), M.A.(Oxon), Ph.D., an orthopedic surgeon at the University of Oxford, told OTW. “Now more than ever is it important to work out what is really necessary, both in terms of follow-ups and devices,” Daniel Perry, M.B.Ch.B. Thats because their bones are softer and more flexible than adult bones. Who Gets Buckle Fractures This type of fracture usually happens in children under 10 years old. One side of a bone bends, raising a little buckle, without breaking the other side of the bone. If an x-ray shows this type of fracture, a splint will be put on the arm to help keep the bone protected. What Is a Buckle Fracture A buckle (or torus) fracture is a type of broken bone. It is an incomplete fracture that normally heals within 1 month. The study, “ Immobilisation of torus fractures of the wrist in children (FORCE): a randomised controlled equivalence trial in the UK,” appears in the July 2, 2022, edition of The Lancet. A distal radius buckle (torus) fracture causes one side of the bone to bend but does not actually break through the bone. A research team in the UK collected data for pain and function in 965 young patients who were offered a soft bandage and immediate discharge and compared those data with children who had been treated for the same fractures with rigid immobilization and follow-up. To be sure, there is disagreement among clinicians regarding the optimal treatment for torus (buckle) fractures of the wrist in children. A new study out of the UK, using data from a recently completed large, randomized study of pediatric forearm fractures (FORCE) has come to the conclusion that, yes, splints do not improve torus fracture outcomes in children.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
